PID Skitter Robot Controller
Designing an autonomous controller for a line-following and object-tracking robot
Project Overview
Role
As a member of a team, I was responsible for designing the control structure and state machine logic for the robot, including the implementation of PID controllers and friction compensation.
Project Duration
Fall 2024 Semester
Key Skills
Control Systems · PID Controllers · State Machine Logic · Sensor Integration (Encoders, Ultrasonic, Line Follower) · Arduino Programming · Engineering Report Writing
Tools/Software
Arduino Mega · Simulink · DC Motors with Encoders · Ultrasonic Sensor · Line Follower Sensor
Project Description
The Challenge
The primary goal of this project was to design and program a controller for the Skitter robot to operate autonomously through a series of tasks. The robot needed to first follow a line around a track for one full lap, then seamlessly transition to a second mode where it would track and follow an object in front of it. This required a robust control system that could integrate multiple sensors and manage different operational states.
The Approach
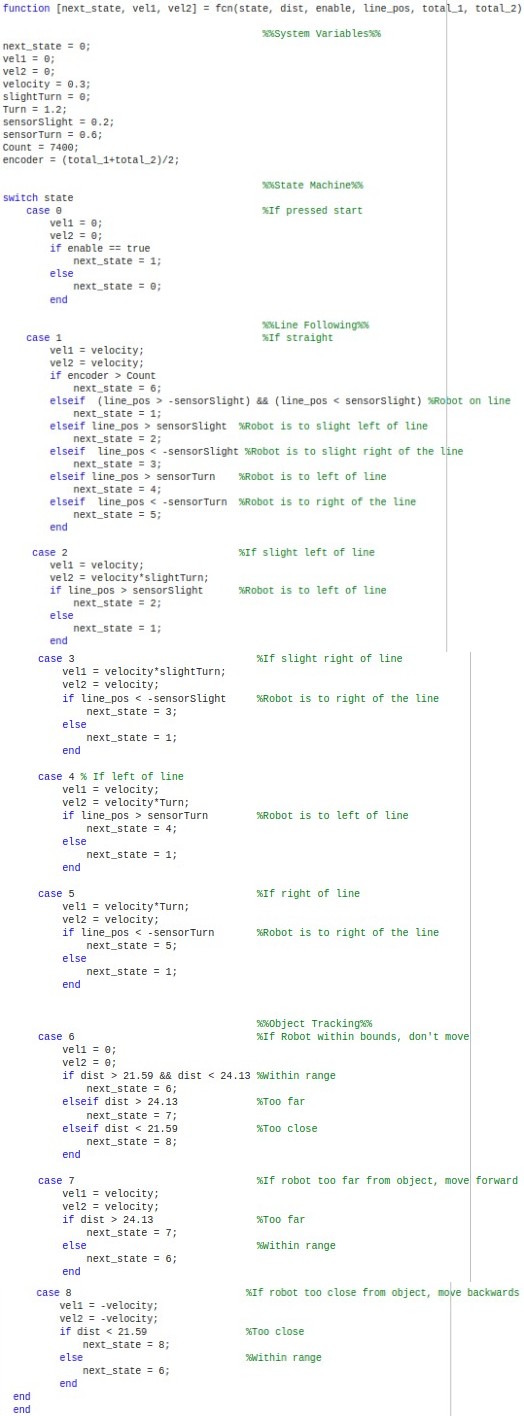
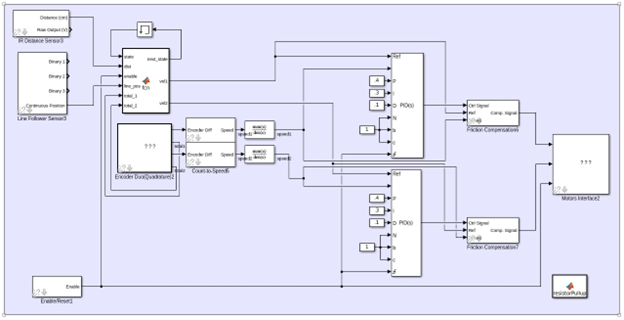
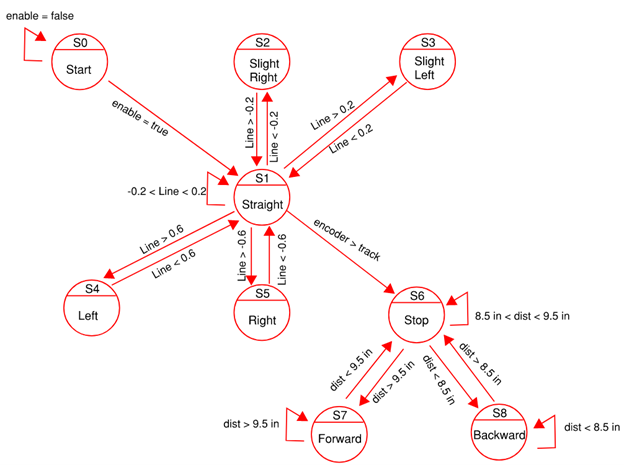
The control system was built around a state machine that dictated the robot’s actions based on real-time sensor inputs. For the line-following portion, the robot used a line follower sensor to make micro-adjustments to its wheel speeds to stay on the track. The movement was divided into five distinct states (e.g., Straight, Slight Right, Large Left) to ensure accurate navigation. After one lap was completed, the encoder values from the wheels were used to trigger the transition to the object-tracking mode. In this mode, an ultrasonic sensor was used to maintain a distance of approximately 9 inches from an object, with the robot moving forward, backward, or stopping as needed. We used PID controllers to regulate the motor speeds and friction compensation to ensure smooth, precise movements in both modes.
The Outcome
The project successfully delivered a working controller that allowed the Skitter robot to perform both line-following and object-tracking tasks autonomously. The state machine proved effective at managing the robot’s behavior, and the use of PID control and friction compensation resulted in stable and accurate movements. While some challenges, such as potential encoder drift and sensor miscalibration, were identified, the control system was designed with a robust framework for testing and fine-tuning. This project provided hands-on experience in applying foundational control systems concepts to a practical robotics application.
Visual Showcase
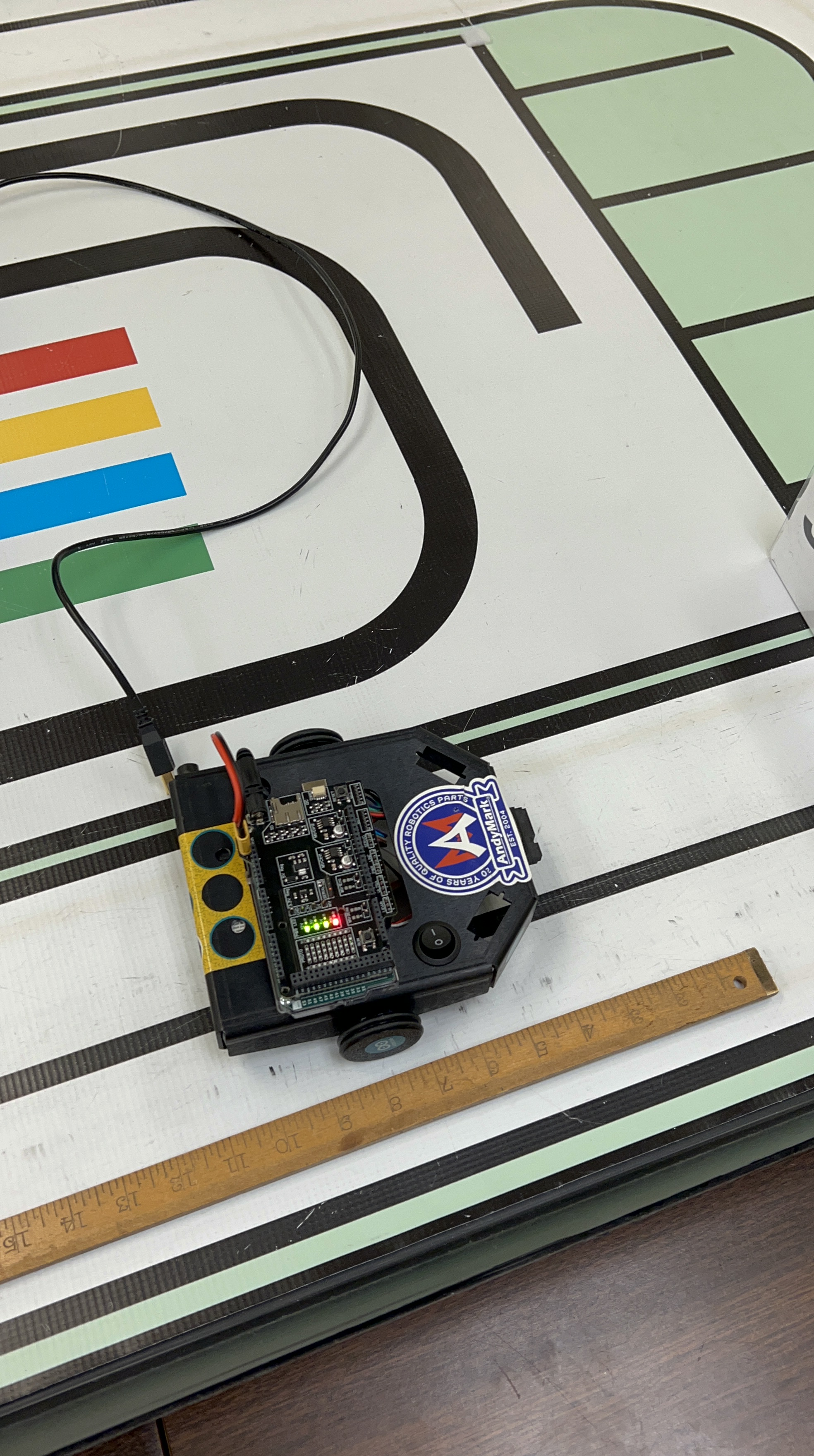


Official Report
If you would like to review the full details of this project, you can download the complete report here:
